Slot of an electric machine
QuickField simulation example
This is an example of the slot of an electric machine simulation, performed with QuickField software.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of heat transfer with convection.
Geometry
All dimensions are in millimeters. Domain is a 10-degree segment of the stator section. Two armature bars laying in the slot generate ohmic loss. Cooling is provided by convection to the axial cooling duct and both surfaces of the core.
Given
Specific copper loss Q = ρ*j*j = (1 / 56MS/m) * 3A/mm² * 3A/mm² = 160 kW/m³;
Thermal conductivity of materials: steel 25 W/K-m, copper 380 W/K-m, insulation 0.15 W/K-m, wedge 0.25 W/K-m.
Outer stator surface convection coefficient 10 W/K-m², air temperature 20°C.
Cooling duct convection coefficient 50 W/K-m², air temperature 40°C.
Inner stator surface convection coefficient 70 W/K-m², air temperature 40°C.
Task
Calculate temperature distribution in the stator tooth zone of an electric machine.
Solution
Due to model symmetry only a single slot is included in the model.
QuickField automatically assigns zero heat flux boundary condition on external boundaries.
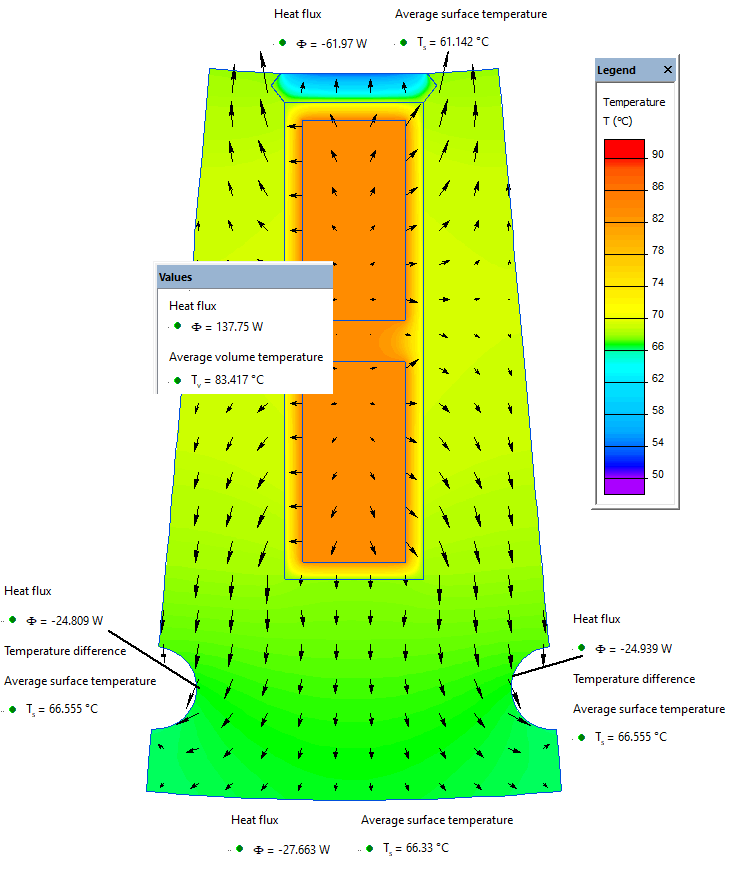
Results
Temperature distribution in a slot of an electric machine:
- Video: Slot of an electric machine. Watch on YouTube
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).