abs - absolute value
| abs(v) = |v| = | v, if v ≥ 0
-v, if v < 0 |
acos - arc cosine
acos(v) = arccos(v)
The function value is equal to arc cosine of the argument in degrees. The argument value v must conform to inequality -1 ≤ v ≤ 1, otherwise an error occurs.
asin - arc sine
asin(v) = arcsin(v)
The function value is equal to arc sine of the argument in degrees. The argument value v must conform to inequality -1 ≤ v ≤ 1, otherwise an error occurs.
atan - arc tangent
atan(v) = arctan(v)
The function value is equal to arc tangent of the argument. The value is given in degrees.
atan2 - arc tangent with two
arguments
atan(v1,v2) = arctan(v1/v2)
The function value is equal to the angle between the x-axis and the direction from coordinate origin to the point with ordinate v1 and abscissa v2. The value is given in degrees and is always between 0 and 360. If both arguments are zero, the value is also zero. Otherwise, if v2 is zero, the value is 90, for positive v1, or 270, for negative v1.
cos - cosine
cos(v)
The function value is equal to cosine of the argument. The argument is defined in degrees.
exp - exponent
exp(v) = ev
The function value is equal to exponent of the argument. Calculation might cause the overflow error.
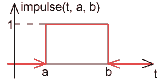
impulse - impulse segment
| impulse(t,a,b) = | 0, if t < a
1, if a ≤ t ≤ b 0, if t > b |
log - natural logarithm
log(v) = ln(v)
The function value is equal to natural logarithm of the argument. The argument value must be positive, otherwise an error occurs.
max - maximum
max(v1,..)
The function value is equal to the maximum of all arguments. You can specify 2 or more arguments.
min - minimum
min(v1,..)
The function value is equal to the minimum of all arguments. You can specify 2 or more arguments.
pow - raising to a power
pow(v,p) = vp
The function value is equal to the first argument value raised to the power defined by second argument value. An error occurs unless the arguments conform to the following conditions: the first argument is non-negative; and if the first argument value is 0, the second argument must be positive. Calculation might cause the overflow error.
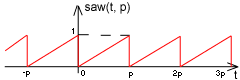
saw - saw-tooth periodic function
| saw(t,p) = | t/p, if 0 ≤ t < p
saw(t+p,..), if t < 0 saw(t-p,..), if t ≥ p |
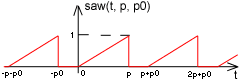
| saw(t,p,p0) = | t/p, if 0 ≤ t < p
0, if p ≤ t < p+p0 saw(t+p+p0,..), if t < 0 saw(t-p-p0,..), if t ≥ p+p0 |
sign - sign
| sign(v) = v/|v| = | 1, if v > 0
0, if v = 0 -1, if v < 0 |
sin - sine
sin(v)
The function value is equal to sine of the argument. The argument is defined in degrees.
sqrt - square root
sqrt(v) = √v
The function value is equal to square root of the argument. The argument value must be non-negative, otherwise an error occurs.
step - step-function with step value equal to 1
| step(t) = | 1, if t ≥ 0
0, if t < 0 |
tan - tangent
tan(v)
The function value is equal to tangent of the argument. The argument is defined in degrees. If argument value is an odd multiple of 90° an error occurs.
See also Formula examples.