Thermal issues in the design of permanent magnet based electrical motors
QuickField simulation example
36 poles brushless DC motor with NdFeB permanent magnets.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of DC magnetics and heat transfer.
Geometry
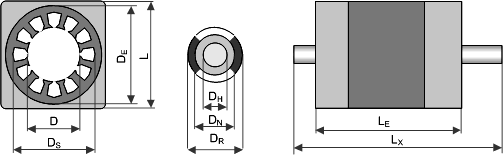
Stator
| Rotor
|
Given
DC motor power P = 12 kW
Voltage U = 600 V;
Speed Nn = 200 rpm;
Torque Mn = 573 N·m;
Insulation class: f (155°C);
Steel power loss (50 Hz, 1.6 T) pf = 5 W/kg;
Air temperature T = 40°C.
Task
Which temperature will afford the magnets under the following working conditions:
Cooling: natural / forced
Load: permanent / periodic (50%)
Results
Rotor final temperature.
| Natural convection
Periodic load | Natural convection
Permanent load | Forced convection
| Forced convection
Permanent load | |
| Winding | 335°C | 375°C | 142°C | 155°C |
| Magnets | 335°C | 385°C | 125°C | 140°C |
| Hub | 342°C | 395°C | 133°C | 147°C |
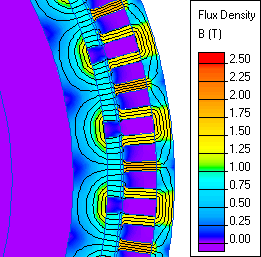
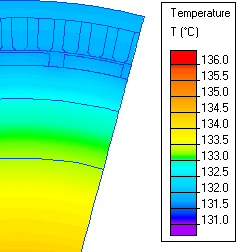
One has to keep in mind the use of forced air circulation as a normal procedure. The controller could offer additional options to pose a limit to currents and/or temperatures.
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).