Electromagnetic simulation of Duffing lock
QuickField simulation example
Duffing's electromagnetic lock is a kind of electromagnet used to permanent attraction of magnet keeper and it fast releasing when additional coil will be energized.
A holding coil is constantly supplied with properly chosen current that saturates relatively thin iron core in the surroundings of releasing coil. If additional current flows there, a magnetic field will be significantly reduced. If the force of keeper attraction is comparable with the force of the spring, even small demagnetizing current will release the magnet keeper.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel nonlinear DC magnetics.
Geometry of the electromagnetic lock:
Model depth 50 mm.
Given
Holding coil total (n*I)h = 100 kA-turns;
Releasing coil total current (n*I)r = 50 kA-turns;
Force of stretching spring f = 250 N/m
Core and keeper iron magnetic permeability - nonlinear:
Results
When releasing coil is not energized (I=0, edlock_1 case) then the force of keeper attraction is about 295 N/m. Otherwise (I>0, edloc_2 case) the attraction force decreases to 225 N and becomes less then stretching force of the spring, and magnet keeper will be unlocked. The force was calculated by means of "Integral calculator" tools.
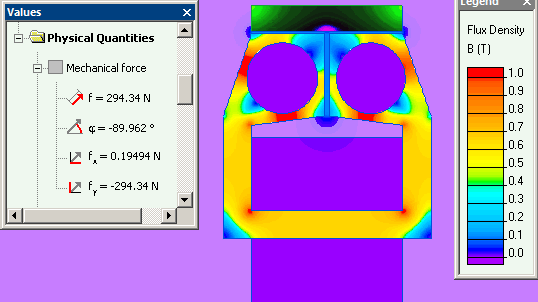
| Ih, A·turns | Ir, A·turns | F, N/m |
| 100000 | 0 | 295 |
| 100000 | 50000 | 225 |
- Video: Electromagnetic simulation of Duffing lock
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).