Two conductors PCB line
QuickField simulation example
This is an example of the two conductors PCB line simulation, performed with QuickField software.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of electrostatics.
Geometry
The problem's region is bounded by ground from the bottom side and extended to infinity on other three sides.
Model depth L = 1 m.
Given
Relative permittivity of air ε= 1;
Relative permittivity of dielectric ε= 2.
Task
Determine self and mutual capacitance of conductors.
Solution
To avoid the influence of outer boundaries, we'll define the region as a rectangle large enough to neglect side effects. To calculate the capacitance matrix we set the voltage U = 1 V on one conductor and U = 0 on another one.
Self capacitance: C11 = C22 = Q1 / U1 ,
Mutual capacitance: C12 = C21 = Q2 / U1 ,
where charge Q1 and Q2 are evaluated on rectangular contours around conductor 1 and 2 away from their edges. We chose the contours for the C11 and C12 calculation to be rectangles [-6<x<0],
Results
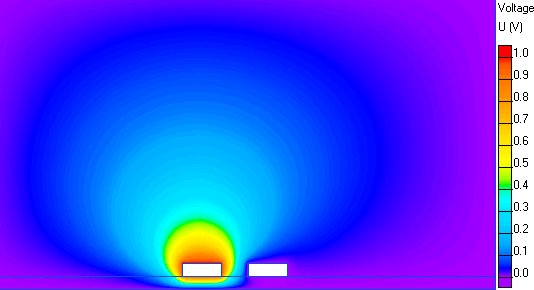
Potential distribution in two conductors transmission line:
| C11, F | C12, F | |
| Reference* | 9.23·10-11 | -8.50·10-12 |
|---|---|---|
| QuickField | 9.43·10-11 | -8.57·10-12 |
* Reference: A. Khebir, A. B. Kouki, and R. Mittra, An Absorbing Boundary Condition for Quasi-TEM Analysis of Microwave Transmission Lines via the Finite Element Method, Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 1990.
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).