Dielectric loss in cable
QuickField simulation example
IEC 60287* suggests that for unfilled XLPE cables rated above the 127 kV level dielectric losses should be calculated.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of AC conduction.
Geometry
Cable length is 1 km
Given
Voltage U = 132 kV (r.m.s.), frequency f = 50 Hz.
XLPE permittivity 2.5, loss tangent tan(δ) = 0.001
Task
Calculate the capacitance and dielectric losses in the cable.
Solution
In AC conduction problem we should specify the electric potential amplitude, which is U * √2.
Electrical conductivity of materials should be set in AC conduction problems. We can take into account dielectric losses by specifying the apparent value of the conductivity**:
σ = 2πf·εε0·tan(δ) = 2*3.142*50*2.5*8.854e-12*0.001 = 6.95 pS/m.
Capacitance = charge / potential difference.
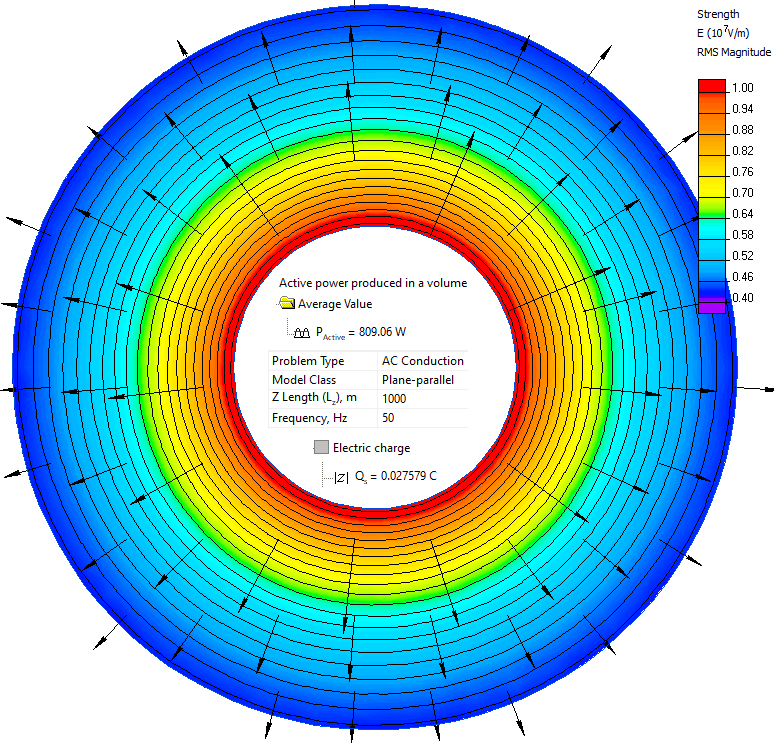
Results
Cable dielectric losses are 809 W per 1 km of the cable length.
Conductor-to-screen capacitance is C = 0.02758 / (132000* √2) = 0.148 μF per 1 km of the cable length. Reference*** value is 0.147 μF/km.
References:
*IEC 60287-1-1. Electric Cables - Calculation of the current rating.
** Wikipedia, Dielectric loss.
*** XLPE Al single core 76/132 kV cable datasheet.
- Video: Dielectric loss in cable. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).