Faraday cage
QuickField simulation example
Electromagnetic fields, generated by high voltage transmission line may affect the human health, and national and international standards regulate the allowed levels of the electromagnetic field exposure to workers. In the European Union corresponding standard is DIRECTIVE 2013/35/EU OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 26 June 2013 on the minimum health and safety requirements regarding the exposure of workers to the risks arising from physical agents (electromagnetic fields). This directive describes the exposure limit levels, which do not produce any sensory and health effects, and action levels, which require special precautions and special measures to be taken.
One of the methods of decreasing the electromagnetic field levels for the personnel, who work with high voltage equipment, is the "Faraday Cage". This is a net made from the grounded conductors, placed between the high voltage conductors and the personnel.
Problem Type electrostatics.
Geometry 3D extrusion.
Given
Relative permittivity of air εr = 1,
Transmission line potential V = 330 kV (RMS, line voltage).
Ground voltage, cage voltage - 0 V.
Task
Calculate the electric field stress distribution under the Faraday cage and compare the electric stress at the height 2 m with the safe level 10 kV/m.
Solution
Line voltage is measured between phase conductors. The phase voltage (between phase conductor and ground) is √3 times smaller than the line voltage.
In QuickField we should specify peak value of the voltage (*√2).
The protected equipment/personnel are not included in the model.
Results
Equipotential surfaces around the Faraday cage.
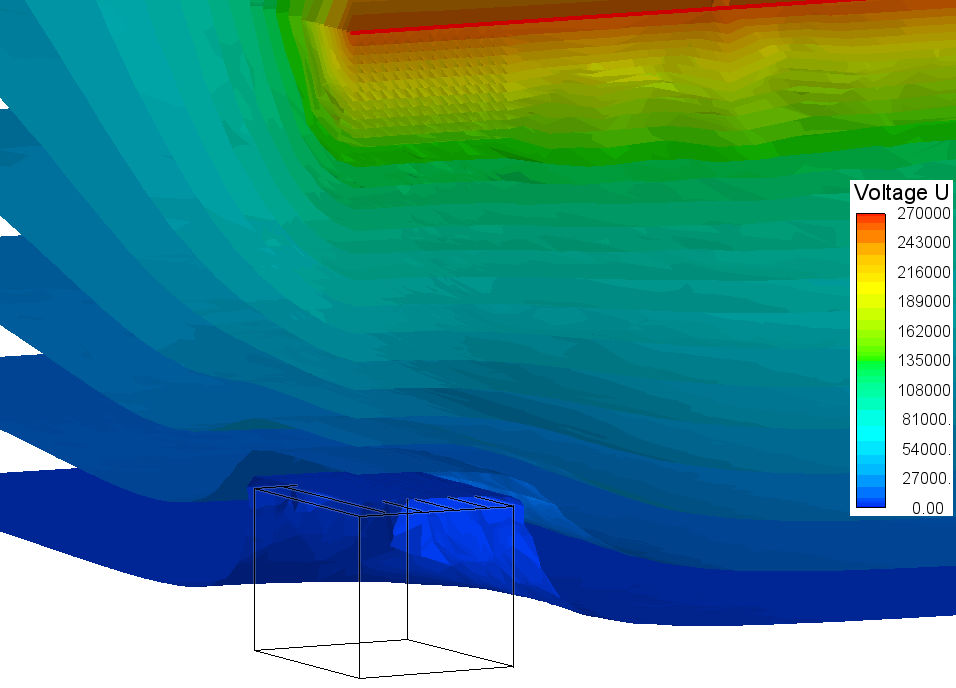
Electric field stress inside the Faraday cage.

*Reference: Faraday cage in Wikipedia.
- Video: Faraday cage. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).