Electric heating film for glass
QuickField simulation example
Electric current is passing through the conductive thin film with two electrodes attached.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of DC conduction.
Geometry
Given
Indium tin oxide film thickness t = 170 nm, sheet resistance Rs = 12.6 Ω/sq.
Electrode thickness d = 2 μm, copper electric conductivity σ = 56 MS/m.
Voltage V+ = 220 V.
Task
Calculate the current and the Joule heat power.
Solution
Film resistivity* ρ = Rs * t = 12.6 * 170e-9 = 2.142 μΩ*m. In QuickField DC conduction analysis we specify the electrical conductivity, that is reciprocal to the resistivity σ = 1 / ρ = 1/2.124e-6 = 467 kS/m.
Electrodes and film thickness are different. To be able to simulate this model in 2D we reduce the electrodes thickness to that of the film and proportionally increase the conductivity σ*d/t = 56 MS/m * 2μm/170nm = 659 MS/m.
Heat power distribution in the film is not uniform, so is the temperature. To get accurate results that take into account the heat redistribution inside the glass we should simulate a 3D heat-transfer problem.
Alternatively we can ignore the fact that the heat is redistributed in the glass and use this example to remap volume heating power Q to temperatures.
First we convert volume power to a surface power q[W/m²] = Q [W/m³] * t [m]
Then we can use the data from the table to get temperature values.
| q W/m² | Glass temperature | |
|---|---|---|
| Inner side | Outer side | |
| 0 | -5.56°C | -7.13°C |
| 1000 | 29.5°C | 22.08°C |
Result
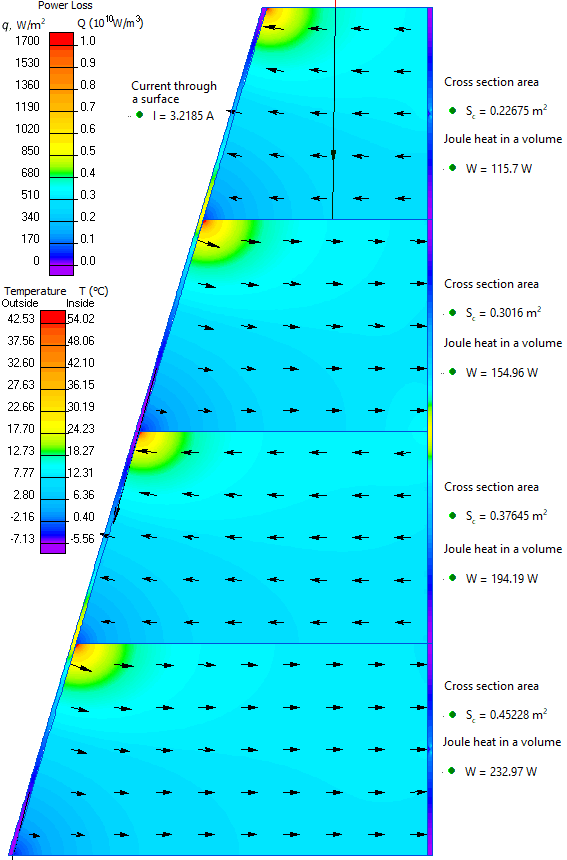
Electric current is I = 3.218 A. Total power is 220 V * 3.218 A = 708 W.
| Section | Area, m² | Power, W | Power/Area, W/m² |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 (top) | 0.22675 | 115.7 | 510 |
| #2 | 0.3016 | 154.96 | 514 |
| #3 | 0.37645 | 194.19 | 516 |
| #4 (bottom) | 0.45228 | 232.97 | 515 |
| Total | 1.357 | 697.82 | - |
The difference (708 - 697.82) W is dissipated in the copper electrodes.
References:
* Wikipedia, Sheet resistance.
- Video: Electric heating film for glass. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).