Lead-acid battery internal resistance
QuickField simulation example
Lead-acid battery consists of two lead grid plates submerged into the electrolyte - concentrated aqueous sulfuric acid solution. Positive plate is covered by the lead dioxide which is formed by the chemical reaction during the charge process, and second grid plate is a negative electrode.
Problem Type
3D problem of DC conduction.
Geometry
Given
Electric conductivity of lead 4.8 MS/m;
Electric conductivity of electrolyte 30 S/m;
Task
Calculate the resistance of the cell.
Solution
To calculate the resistance we can apply a potential difference ΔV and measure the electric current value I. The resistance of a cell is then R = ΔV / I
We choose V+ = 1 V and V- = -1 V. So the potential difference is
ΔV = (V+) - (V-) = 2 V.
The model features symmetry, so only a positive grid-electrode is shown. On the plane of symmetry the U = 0V boundary condition is set.
Results
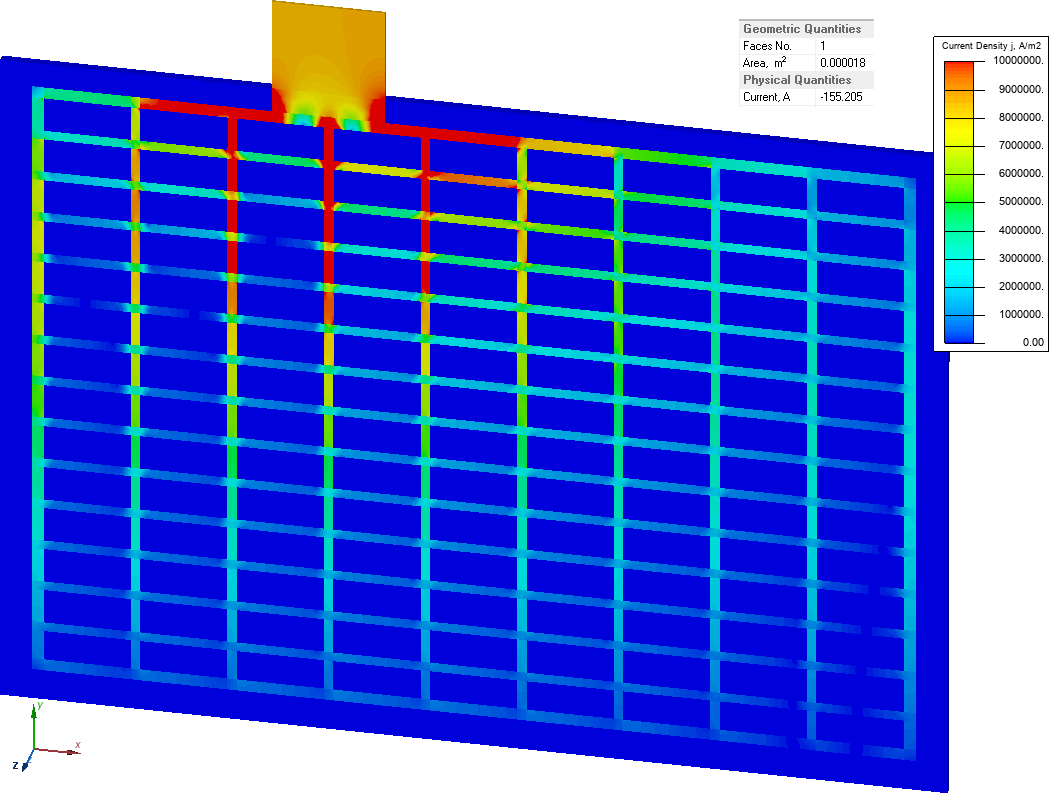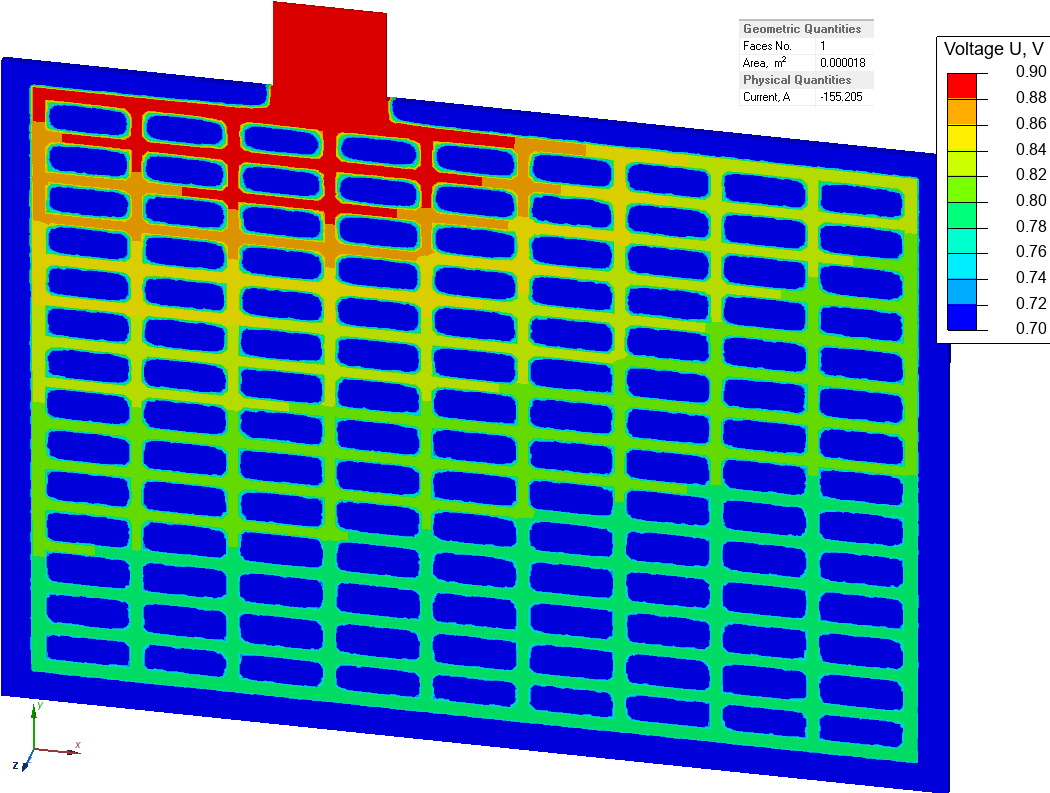
Electric current value is 155 A. Resistance of the cell is R = 2/155 = 12.9 mOhm.
Current density and electric potential distribution in the grid electrode
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).