Pair of parallel wires capacitance
QuickField simulation example
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of electrostatics.
Geometry
a1 = 4 mm, a2 = 1 mm, b = 10 mm.
Given
Relative permittivity of air ε = 1,
Charge value q = 1 nC.
Task
Find the mutual capacitance between two parallel wires and compare its value with analytical solution*:
C/Lz = 4π·ε·ε0 / 2·LN [ (b²-a1²-a2² + 2bc) / 2·a1·a2 ] [F/m],
where 2bc = √
Solution
Wire's surfaces are marked as 'floating conductor', i.e. isolated conductors with unknown potential. At some point on each of wire's surface the charge q is applied. The charge is then redistributed along the conductor surface automatically.
QuickField calculates electric potential U distribution. The capacitance is calculated as C = q / ΔU.
In problem properties we set model depth to be Lz = 1 m.
Results
Analytical solution 2bc = √
C/Lz = 4·3.142·1·8.854e-12 / 2·LN [ (0.01²-0.004²-0.001² + 8.261e-5) / (2·0.004·0.001) ] = 18.36 pF/m.
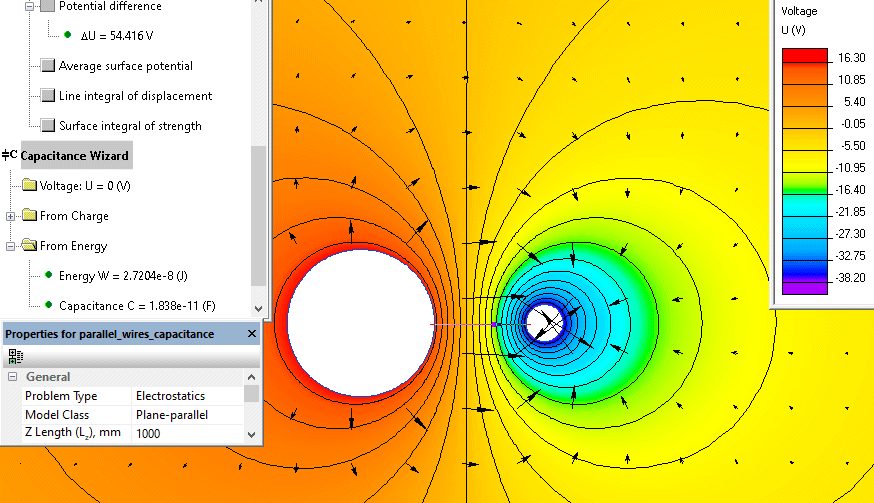
The measured potential difference in QuickField is ΔU = 54.41 V.
The capacitance is C = 1 nC / 54.41 V = 18.38 pF per model depth Lz = 1 m.
Electric potential distribution around parallel wires calculated in QuickField:
*Reference: Chester Snow Formulas for Computing Capacitance and Inductance, U.S. Government Printing Office, 1954
- Video: Pair of parallel wires capacitance. Watch on YouTube
. - View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).