PCB hatched ground plane electrical resistance
QuickField simulation example
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of DC conduction.
Geometry
Plane consists of the copper hexagonal cells with dimensions shown in the picture below. Plane thickness is 35 micrometers.
Given
Electric conductivity of copper σ = 56 MS/m;
Task
DC current is flowing across the rectangular plane 180mm x 100mm between the electrodes welded to the diagonal corners. Calculate the electric resistance.
Solution
Solution is based on the analysis of the currents flowing in the solid plane with equivalent electric conductivity. Task is performed in two steps.
- First we analyze the DC currents in the small square fragment of the hatched plane 4.8 mm by 4.8 mm. At the top side the square the positive potential of 1 mV is applied, bottom side is grounded (0 V). The current value is then calculated, which gives us the hatched plane fragment resistance.
R_ = ΔU / I
While the same size copper square resistance may be calculated analytically as
R = (1/σ) * Length / Cross-section area
Comparison of the calculated hatched plane fragment resistance and solid copper fragment resistance gives us the equivalent value of the hatched plane material conductivity. - Then other QuickField problem is prepared where the current is flowing in the solid plane with equivalent conductivity and the resistance is found as ratio of the potential difference and current coming into the electrode.
Results
Step 1 problem:
Solid plate resistance: R = (1/56e6) * 4.8e-3 / (4.8e-3 * 35e-6) = 0.51 mOhm.
Hatched plane resistance: R_ = 0.001 / 0.31 = 3.2 mOhm
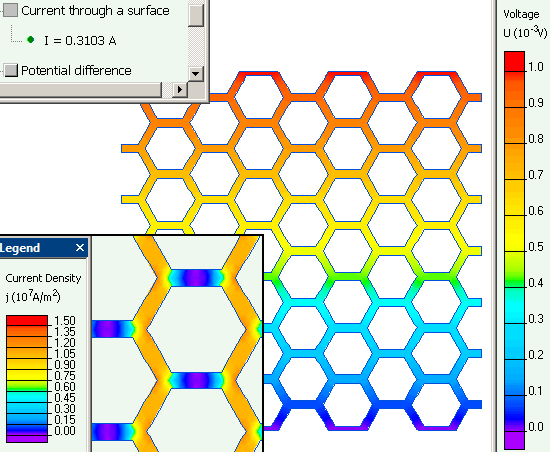
Equivalent conductivity of the hatched plane material
γ_ = γ * (R/R_) = 56 MS/m * (0.51 mOhm / 3.2 mOhm) = 8.9 MS/m.
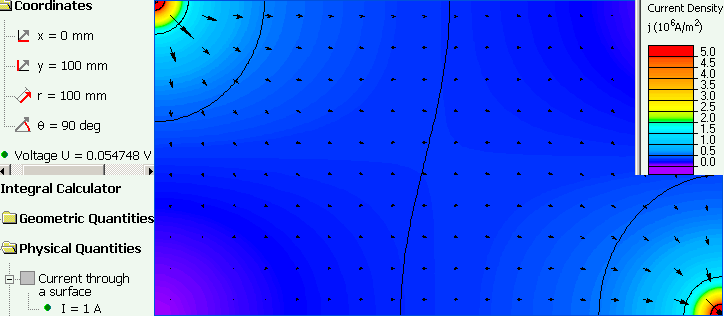
Step 2 problem.
Resistance = Voltage drop / Current = 0.054 V / 1 A = 54 mOhm
- Video: PCB hatched ground plane electrical resistance. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).