Potential transformer electric stress
QuickField simulation example
Potential transformer or voltage transformer* is an instrument transformer used to measure the high voltage. The primary high voltage winding has a large number of turns and features a special form factor to reduce the electric field stress.
The primary high voltage winding has a large number of turns and features a special form factor to reduce electric field stress. One end of the winding is connected to the mains and the other end is grounded. The electric potential is distributed linearly along the winding. There are 35000 turns in the primary winding and 100 turns in the secondary.
Problem Type
Axisymmetric problem of Electrostatics.
Geometry
Given
High voltage is 35 kV. Transformation ratio is 350:1.
Dielectric permittivity of media: oil 2.3, paper + oil 2.3, cardboard 2, conductor insulation 3.
Task
Calculate the electric stress distribution.
Solution
The electric potential is linearly distributed along the primary winding. We do not draw each individual conductor. Instead we draw each individual layer and specify the electric potential as a function of coordinates.
The transformer operates at AC voltage. We simulate a single moment of time, when the voltage value is equal to 35 kV. So, we use the Electrostatics module of QuickField.
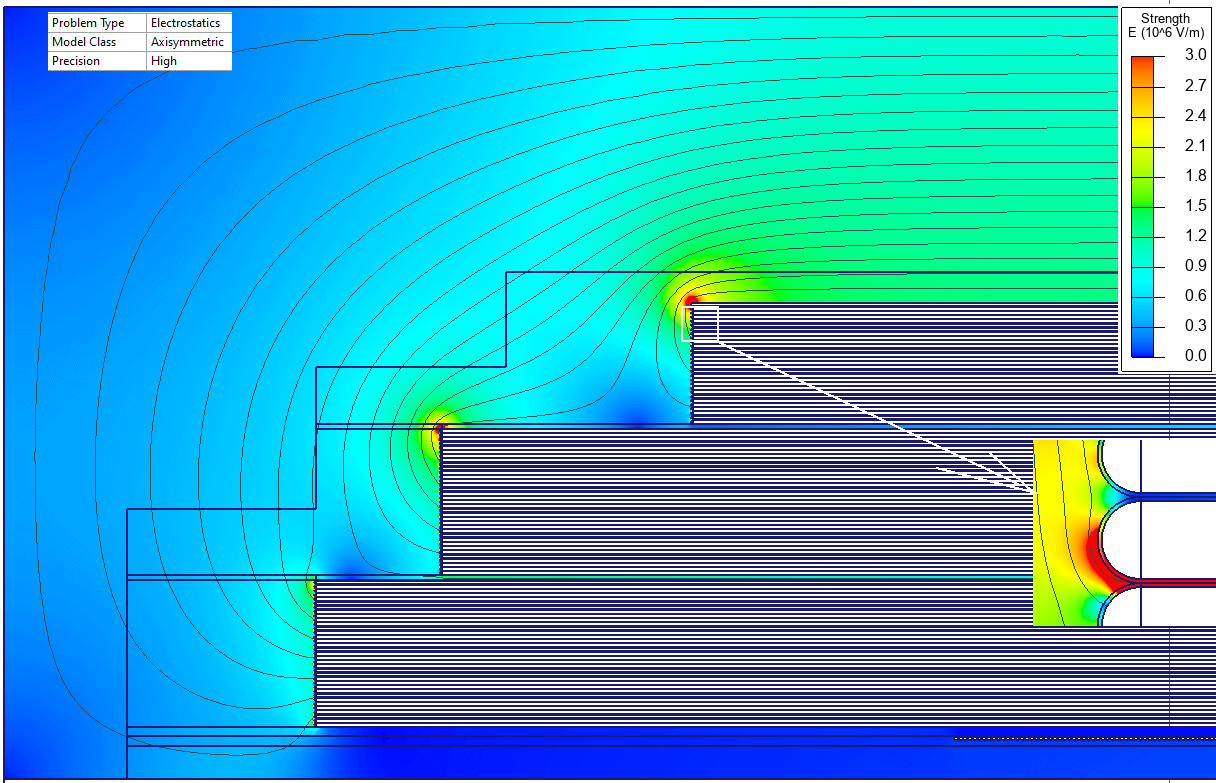
Results
The most stressed part is the insulation between the adjacent winding layers. The stress value there is 10 kV/mm.
* Reference
Wikipedia: Voltage transformer
- Video: Potential transformer electric stress. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).