Touchless sensor
QuickField simulation example
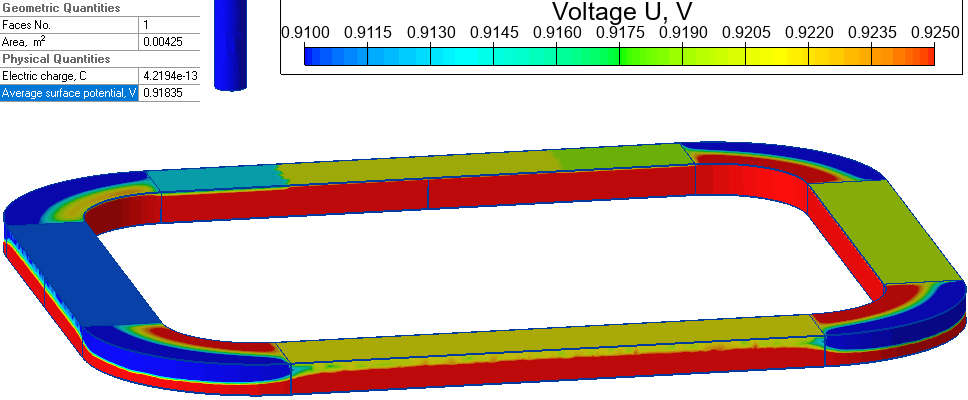
Touchless sensor consists of two groups of electrodes on the sides of the rectangular dielectric frame. Tx - transmitter, with voltage applied, Rx - receivers. Rx potential depends on the position of the finger near the sensor.
Problem Type
3D problem of electrostatics.
Geometry
Distance between the finger and the sensor surface is 50 mm.
Given
Relative permittivity of dielectric ε= 4.7
Tx voltage +1V, Rx - floating, finger is grounded.
Task
Determine Rx electrodes potential for various finger positions.
Solution
Real sensor operates at AC voltage and the potential difference between Rx and Tx electodes are measured. As materials conductivity is almost zero we can safely ignore active component of the electric current and switch to the electrostatic analysis.
A set of problems is simulated with different finger positions. Due to the model symmetry we simulate only the cases where thefinger placed in the top left quarter of the sensor window. QuickField calculates the average surface potential for each of Rx electrodes.
Results
Electrodes potential (Tx-Rx) for different finger x-position at y = .
Electric field distribution in touch sensor:
- Video: Touchless sensor. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).