Cable thermal resistance
QuickField simulation example
In this example we build thermal model of the high-voltage cable described in the IEC 60853-2 example F2*. Thermal resistances of the cable parts are calculated.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of Heat Transfer.
Geometry
Given
Thermal resistivity of materials [K*m/W]: serving 3.5, oil/paper 5.0, soil 1. The semiconducting screens thermal conductivity is considered to be the same as that of the insulation, 5.0 K*m/W.
Task
Calculate thermal resistances** of the cable parts and compare results with the reference values*.
Solution
Thermal resistance [K*m/W] = Temperature difference [K] / Heat flux per 1 meter of cable length [W/m]
To calculate the thermal resistance we are going to specify heat losses 30 W/m in the conductor and measure the temperature drop in cable layers.
In QuickField we should specify thermal conductivity [W/K*m] of materials, that is reciprocal to the thermal resistivity. Copper conductor thermal conductivity is 380 W/K*m, lead sheath thermal conductivity is 25 W/K*m.
Results
Temperature drop conductor-sheath is (0.614+13.761+0.226) = 14.6°C, thermal resistance conductor-sheath is T1 = 14.6 / 30 = 0.487 K*m/W. Reference value* 0.488 K*m/W.
| Layer | Temperature drop, K | Thermal resistance, K*m/W | |
|---|---|---|---|
| QuickField | Reference* | ||
| Conductor screen | 0.614 | 0.020 | 0.021 |
| Insulation | 13.761 | 0.4587 | 0.459 |
| Core screen | 0.226 | 0.0075 | 0.008 |
| Sheath (lead) | 0.01 | 0.00033 | - |
| Serving | 1.132 | 0.0377 | 0.038 |
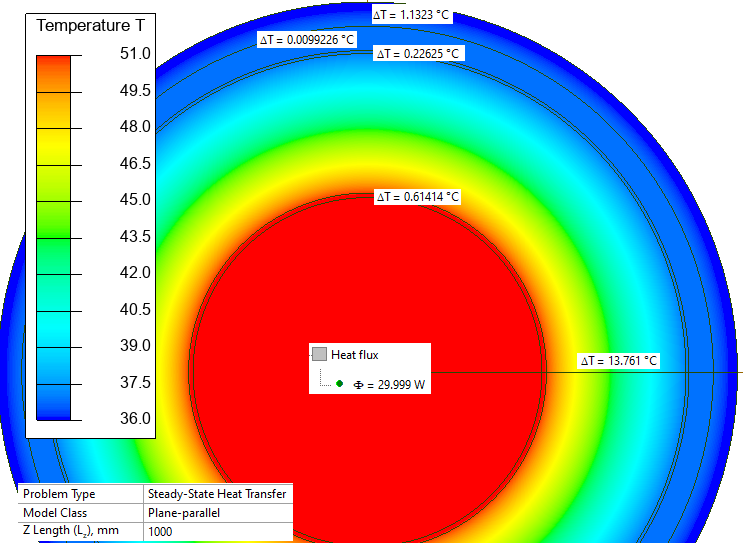
Temperature distribution along the radius of the cable.
References:
* IEC 60853-2, Calculation of the cyclic and emergency current rating of cables. Part 2: Cyclic rating of cables greater than 18/30 (36) kV and emergency ratings for cables of all voltages.
** Wikipedia, Thermal resistance.
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).