Capacitive touch sensor
QuickField simulation example
Capacitive touch sensor consists of two electrodes: transmitting Tx and receiving Rx placed on the dielectric board. Presence of the finger in their vicinity affects the capacitance between electrodes.
Problem Type
3D problem of electrostatics.
Geometry
Given
Relative permittivity of dielectric = 4.7, dielectric board thickness 1 mm
Relative permittivity of coating = 4, coating thickness 0.1 mm
Tx voltage +1 V, Rx voltage 0 V.
Task
Determine the capacitance between transmitting Tx and receiving Rx electrodes of the touch sensor with and without the finger in their vicinity.
Solution
The electrodes are made of conducting foil. We neglect the conducting foil thickness and draw electrodes as zero-thickness surfaces.
For simplicity we approximate the finger shape with a cylinder. Then it is possible to construct the geometry model using 3D extrusion.
Biological tissues show high values of dielectric permittivities (see QuickField Modelling of Electro-Pulse-Therapy), so for the finger we specify the relative dielectric permittivity 10000.
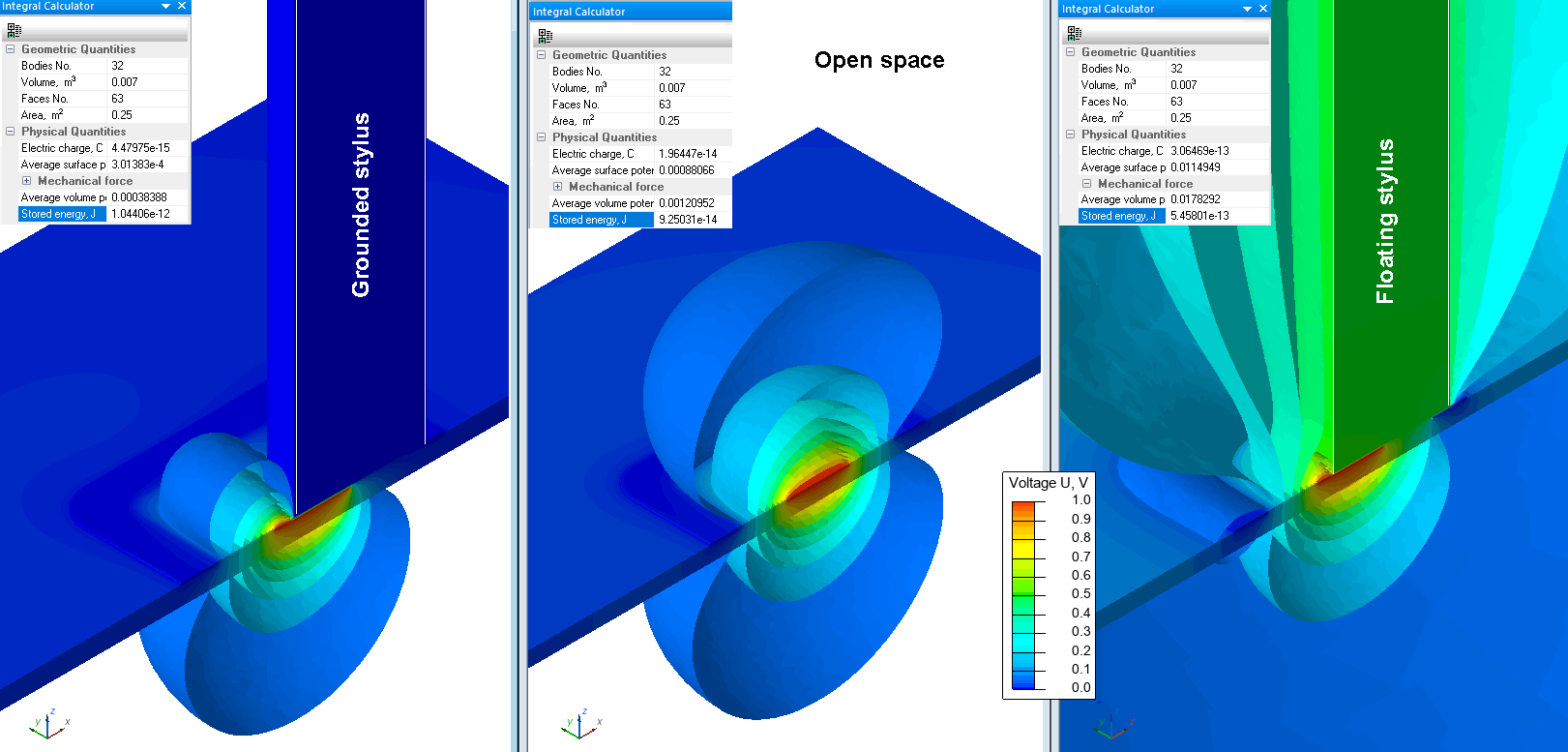
Three situations are analyzed: the finger surface is grounded (zero electric potential), not grounded (floating equal electric potential) and the finger is not present (open space near the conductors).
Capacitance is calculated as C = 2* W / ( ΔU )², where W is a stored electric energy and ΔU is a potential difference between Rx and Tx electrodes
Results
| Electric energy W, pJ | Capacitance, pF C = 2* W / ( ΔU )² | |
|---|---|---|
| Open space | 0.093 | 0.18 |
| Floating cylinder | 0.546 | 1.1 |
| Grounded cylinder | 1.04 | 2.1 |
Electric field distribution near the touch sensor:
- Video: Capacitive touch sensor. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).