Cylindrical rod
QuickField simulation example
Cylindrical rod is loaded by tensile forces.
Problem Type
Axisymmetric problem of stress analysis.
Geometry
Given
Rod's length L=3000 mm, cross-section diameter d = 30 mm;
Young's modulus of the aluminum alloy E = 70 GPa;
Poisson's coefficient of the aluminum alloy ν = 1/3;
Force P = 85 kN.
Task
Calculate bar elongation, the decrease in diameter and the increase in volume.
Solution
One of the rod's ends is fixed. The other end is loaded by the tensile force fz = P / S,
where S= 786·10-6 [m²] - is the rod cross-section area.
Volume change can be calculated by the length dL and width dr increments:
dV = (L+dL)·π·(R+dr)² - L·π·R².
Results
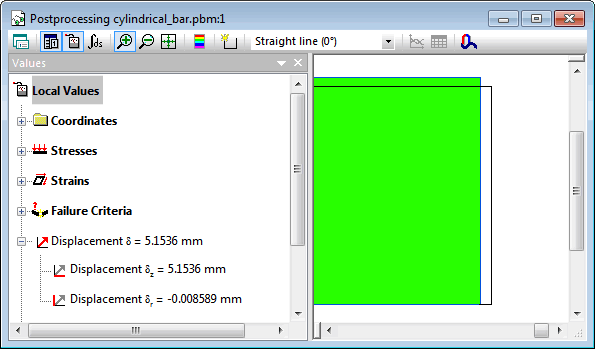
Volume change dV = (3000+5.1536)·π·(15-0.008589)² - 3000·π·15² = 1210.91 mm³.
| Elongation dL, mm | Decrease in diameter 2·dr, mm | Increase in volume dV, mm³ | |
| QuickField | 5.1536 | 0.017178 | 1210.9 |
| Theory* | 5.1557 | 0.017186 | 1214.8 |
| Error | 0.04% | 0.05% | 0.3% |
* James M. Gere, Stephen P. Timoshenko Mechanics of materials, Third edition (1990), pp.26-27. ISBN:0-534-92174-4.
- Video: Cylindrical rod. Watch on YouTube
.- Video: Hooke's law. Watch on YouTube
. - View simulation report in PDF.
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).
- Video: Hooke's law. Watch on YouTube