Fick's laws of diffusion
QuickField simulation example
An example is devoted to modeling the diffusion of water through a concrete wall. The diffusion equation (Fick's law) and the heat transfer equation have similarity. To simulate the diffusion process the heat transfer problem is calculated.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of Transient heat transfer.
Geometry
Given
Initial concrete internal humidity: C0 = 10%;
Diffusion coefficient: D = 0.0001 cm²/s;
Task
Estimate the water penetration into the concrete wall after 5 days exposure.
Solution
The diffusion equation* (Fick's law) for the one-dimensional case is:
dC/dt = D * d²C / dx²,
where C(x, t) is the water concentration, D is the diffusion coefficient.
Heat equation** for the one-dimensional case is:
dT/dt = a * d²T / dx²,
where T(x, t) is the temperature, a is the thermal diffusivity.
The diffusion equation (Fick's law) and the heat transfer equation have similarity. The role of concentration in the diffusion equation is the same as a role of the temperature in the heat transfer equation. And the role of the diffusion coefficient D is performed by the thermal diffusivity, which is calculated as a = λ /Cρ,
where λ is thermal conductivity, C is specific heat capacity and ρ is density.
We can choose any values of λ, C and ρ to achieve the desired thermal diffusivity value. In the thermal problem, the following values were taken to specify the thermal diffusivity 0.0001 cm²/s: λ = 0.028 W/K-m, C = 1273 J/kg-K, ρ = 2200 kg/m³.
a = 0.028 W/K-m / (1273 J/kg-K * 2200 kg/m3) = 1e-8 m²/s = 1e-4 cm²/s
Result
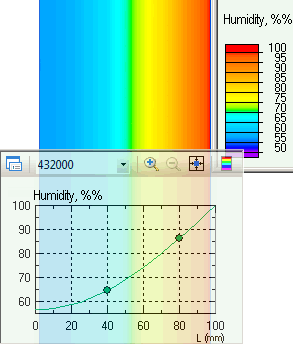
After 5 days, the humidity of concrete on the air-side of the wall will be 56%, and the average volume moisture content will be 72%.
The distribution of humidity (temperature) inside the wall after 5 days exposure is shown in the figure.
Reference
*Wikipedia: Diffusion
**Wikipedia: Heat equation
- Video: Fick's laws of diffusion. Watch on YouTube
. - Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).