Helmholtz coil
QuickField simulation example
A Helmholtz coil is a device for producing a region of nearly uniform magnetic field. This construction is formed by the two identical circular coils, placed symmetrically along a common axis, and separated by the distance H equal to the coil radius R. Both coils carry the same electric current I. Area of the quasi uniform field is located inside the coils.
Problem Type
Axisymmetric problem of DC magnetics
Geometry
Given
H = R = 1 m,
Each coil consists of 1 loop with total electric current of I = 1 A. Media around the coils is air.
Task
Calculate the flux density distribution within the Helmholtz coil. Find the area of uniform field. Compare with analytical approximation.
Solution
Model may be defined and solved as a DC Magnetic analysis problem.
The field within Helmholtz coils at the axis may be estimated as*:
B(x) = 2B1(x) = 2 · μnIR² / 2(R² + x²)3/2
The field at the center between Helmholtz coils is:
B(x=R/2) = 2 · μnIR² / 2(R² + (R/2)²)3/2 = 0.83/2 · μnI/R.
Results
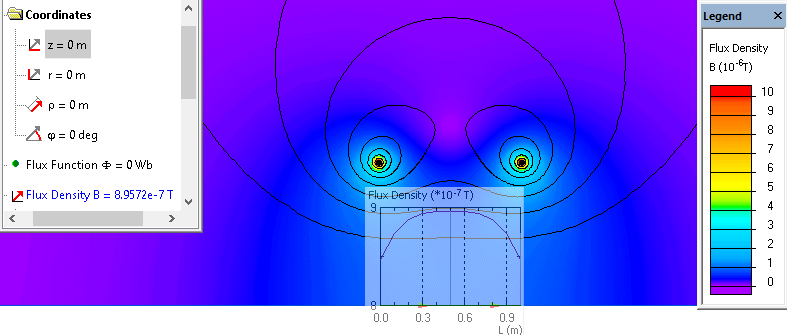
Analytical solution for I=1 ampere, R=1 meter and n=1 gives B(x=0) = 8.98e-7 T.
QuickField calculates flux density value at the center between Helmholtz coils as B = 8.95e-7 T.
Flux density distribution around the Helmholtz coils
* Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Helmholtz_coil
- Video: Helmholtz coil. Watch on YouTube
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).