Pipe outlet thermal losses
QuickField simulation example
Insulated water pipe with non-insulated outlet.
Problem Type
3D problem of heat transfer.
Geometry
Given
Thermal conductivity of steel λsteel=40 W/K-m;
Thermal conductivity of insulation λinsulation=0.1 W/K-m;
Water temperature Twater = 90 °C;
Air temperature Tair = -15 °C, convection coefficient: hair = 20 W/K-m²;
Task
Calculate temperature distribution and heat losses caused by non-insulated pipe outlet.
Solution
Dew to geometrical symmetry we can simplify the model and simulate 1/4 of the full structure.
Additional losses are equal to the difference between losses in fully insulated pipe and the losses in the pipe with outlet.
Heat losses from fully insulated pipe can be calculated analytically:
q [W/m] = (Twater - Tair) / R,
where thermal resistance is R = ln(rsteel/rinner) / 2πλsteel + ln(rinsulation/rsteel) / 2πλinsulation + 1/2πrinsulationhair
Results
Analytically calculated losses of fully insulated pipe are:
q = (90-(-15)) / (ln(0.105/0.1) / 2π*40 + ln(0.155/0.105) / 2π*0.1 + 1/2π*0.155*20) = 156 W/m.
For a piece of pipe L=0.8m the total losses are q * L = 156 * 0.8 = 125 W.
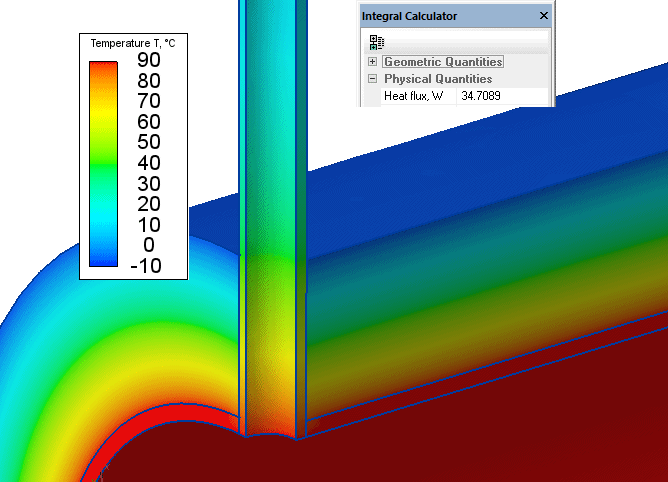
Temperature distribution in a pipe near the outlet. Heat flux value should be quadrupled (since we have only 1/4 of the pipe in the model).
Total heat loss in the pipe with outlet are 34.7 * 4 = 139 W.
The outlet brings additional 139-125 = 14 W of heat losses.
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).