ISO 11855-2:2015. Pipe in the floor
QuickField simulation example
This is a simulation example from ISO 11855-2:2015 Building environment design — Design, dimensioning, installation and control of embedded radiant heating and cooling systems. Part 2: Determination of the design heating and cooling capacity.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of Heat Transfer.
Geometry
Given
Air temperature +26°C, heat exchange coefficient at the top surface αtop = 7 W/m²K, heat exchange coefficient at the bottom surface αbottom = 11 W/m²K,
Water temperature = 18 °C, turbulent flow.
Pipe wall thickness = 2.3 mm
Thermal conductivity λ of materials:
- floor covering, 0.23 W/(m·K)
- screed, 1.2 W/(m·K)
- thermal insulation, 0.04 W/(m·K)
- concrete, 2.1 W/(m·K)
- pipe PE-X, 0.35 W/(m·K)
Task
Calculate temperature distribution in the floor and heat flux at top and bottom surfaces.
Solution
Thermal resistance between water and inner pipe surface is assumed to be zero, so the fixed temperature boundary condition is used.
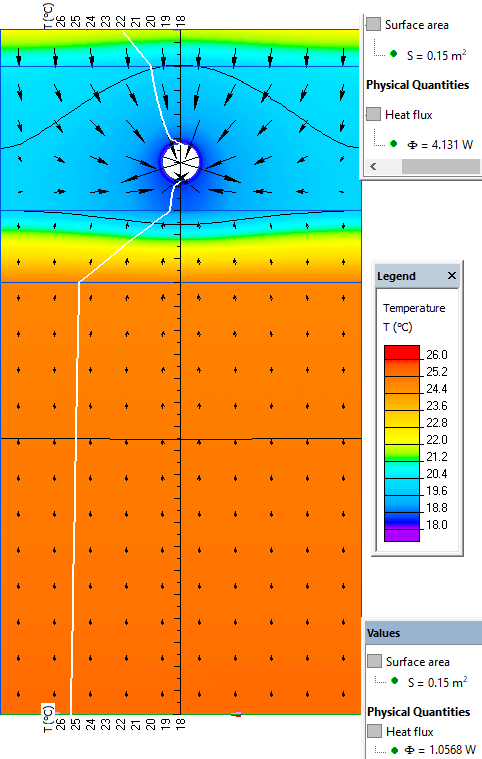
Results
Average heat loss density at the top surface is 4.13 W /0.15 m² = 27.5 W/m² (ISO 11855-2:2015 gives 27.4 W/m²)
Average heat loss density at the bottom surface is 1.05 W /0.15 m² = 7.0 W/m² (ISO 11855-2:2015 gives 7.0 W/m²)
Difference between the calculated and reference values is less than 3%. This simulation accuracy complies with the requirements of ISO 11855-2:2015.
* Reference: ISO 11855-2:2015 Building environment design — Design, dimensioning, installation and control of embedded radiant heating and cooling systems — Part 2: Determination of the design heating and cooling capacity.
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).