Magnetic field of a magnetron sputtering system
QuickField simulation example
The magnetic field of a magnetron should be properly configured to confine electrons close to the target. We calculate the magnetic field distribution and detect the magnetic field unbalance* in this example.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of DC magnetics.
Geometry
Given
Permanent magnets are made of NdFeB N42, coercive force is 860 kA/m, relative permeability is 1.2.
Core relative permeability is 1000.
Task
Calculate the magnetic field distribution and measure the magnetic field unbalance.
Solution
We use the unbalance coefficient proposed by Gencoa Ltd*. The coefficient is calculated as g = ZBz=0 / W½, where ZBz=0 is the distance from target to the point, where magnetic flux z-component is zero, and W½ is the target radius.
Results
ZBz=0 = 12.6 mm. Unbalance coefficient g = 12.6 / 14 = 0.9.
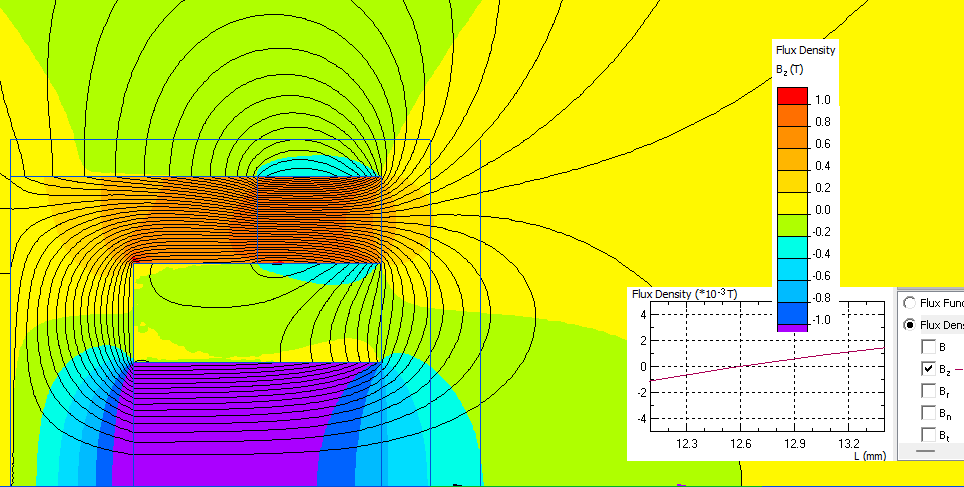
Flux density distribution along the target surface.
References:
* R. Brown, V. Bellido-Gonzalez. Comparison of balanced and unbalanced array designs., Thin film and PV solution, 2013.
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).