Planar heater 3D
QuickField simulation example
The planar heater is placed between two layers of glass of irregular shape. The heater consists of a serpentine stripe carrying electric current. QuickField is used to calculate the temperature distribution in the glass.
Problem Type
A 3D problem of Heat Transfer.
Geometry
There are 10 mm paddings between the glass edges and the heater.
Given
Heater power 600 W/m².
Indoor air temperature is +20°C, convection coefficient is 8 W/m²*K.
Outdoor air temperature is -15°C, convection coefficient is 23 W/m²*K.
Task
Calculate temperature distribution in the glass.
Solution
Film thickness (~0.01 mm) is much less than the glass thickness. So we do not model film as a body, but as a surface with a surface power heat specified instead. For simplicity we assume that the heating power is evenly distributed in the serpentine stripe.
Result
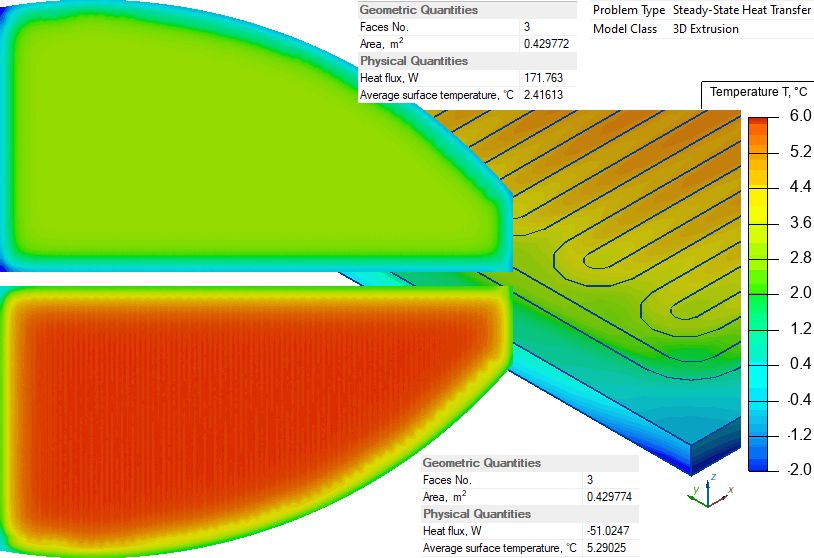
Glass inner surface average temperature is +5.3°C, outdoor surface average temperature is +2.4°C.
Average heat flux generated by the planar heater is (171.76 - 51.02) / 0.42977 = 281 W/m².
- Video: Planar heater 3D. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).