Steam pipe
QuickField simulation example
Steam is passing through the insulated steel pipe. Minimum insulation layer thickness which is required for the allowable heat losses should be found.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of heat transfer.
Geometry
R1 = 60 mm, R2 = 80 mm, R3 = ?
Given
Thermal conductivity of steel λsteel = 42 W/(m·K);
Thermal conductivity of asbestos λasbestos = 0.8 W/(m·K);
Temperature of steam Tsteam = 150°C,
Temperature of air Tair = 20°C,
Convection coefficient on the steam side of the pipe αsteam = 100 W/K-m²,
Convection coefficient on the air side of the pipe αair = 30 W/K-m²,
Allowable power of heat losses f = 2.1 kW/m².
Task
Determine the minimum thickness of the insulation (R3-R2) required for allowable heat losses.
Solution
Heat flux passing through any cross-section of the pipe is the same and could be measured at the pipe's surface. To solve the problem it is enough to take a piece of the pipe with arbitrary length, since the flux per meter of the length is the same. For convenience we choose such a length so that square of the steel surface equals to 1 m², i.e. Lz = 1/(2π·r2) = 2.122 m. In this case the heat flux density is numerically equal to the heat flux.
Search of the optimal solution is automated via utility LabelMover, which creates and solves series of the problems with different values of R3, converging to the heat flux value of 2.1 kW.
Results
Temperature distribution in the pipe walls.
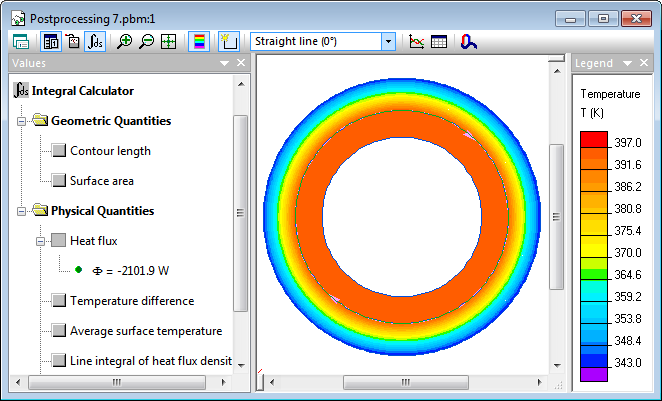
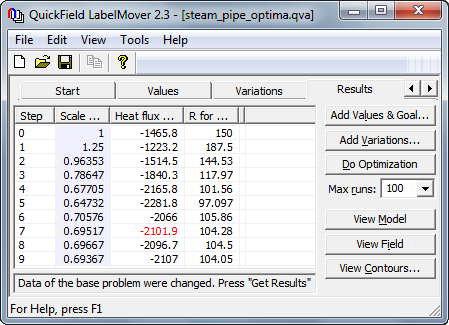
| R3,mm | f, W/m² | |
| QuickField | 104.3 | 2102 |
| Theory* | 105 | 2100 |
| Error | 0.7% | 0.1% |
Reference
* Rajput R.K.(2010). Engineering Thermodynamics, Third Edition. Sudbury, MA:Jones and Bartlett Publishers, p. 813. Example 15.11.
- Video: Steam pipe. Watch on YouTube
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).