Steel tank
QuickField simulation example
The steel tank contains hot water. Determine the wall temperature and heat losses.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of heat transfer.
Geometry
Given
Hot water temperature t°=95°C;
Water-to-wall convection coefficient α = 2850 W/m²°C;
Cooling air temperature 15°C;
Wall-to-air convection coefficient α = 10 W/m²°C;
Wall thermal conductivity λ = 50 W/m·K.
Task
Calculate the average heat flux density passing through the tank wall and the wall air-side temperature.
Solution
To solve the problem it is enough to simulate a small piece of the tank wall. Heat losses (heat flux density) are calculated as a heat flux value divided by the wall surface area value.
Result
Heat flux through the wall is 795 W per 1 meter square, average surface temperature is 94.5°C.
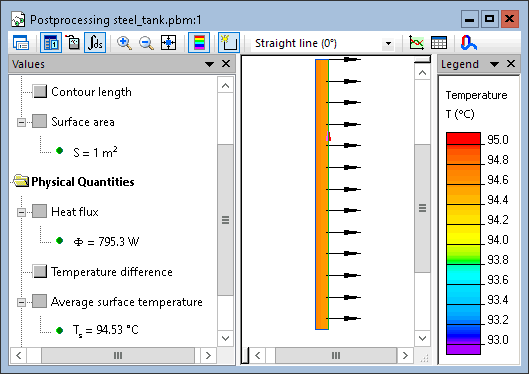
| QuickField | Theory* | Error | |
| Wall outside temperature | 94.53°C | 94.52°C | 0.011% |
| Flux density, W/m² | 795.3 | 795.2 | 0.013% |
*Rajput R.K.(2010). Engineering Thermodynamics, Third Edition. Sudbury, MA:Jones and Bartlett Publishers. Page 805.
- Video: Steel tank. Watch on YouTube
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).