Underfloor heating
QuickField simulation example
Example of a heat transfer simulation for an underfloor heating system.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of Heat Transfer.
Geometry
Given
Air temperature above the floor = 18°C;
Air temperature below the floor = 20°C;
Convection coefficient α = 5 W/m²-K;
Radiation coefficient β = 0.4;
Cable heat power q = 100 W/m.
Thermal conductivity of materials:
Cement 1.4 W/m-K;
Insulation 0.05 W/m-K;
Cable (copper) 401 W/m-K;
Floor slab 1.69 W/m-K;
Task
Calculate the distribution of temperature for underfloor heating and evaluate the efficiency of heating.
Solution
The model represents only a small part of the floor with a size of 1m x 1m.
QuickField takes input of heat power as volume power density in [W/m³], which can be calculated as:
Q = q/Sc, where Sc = π*d²/4 - cable cross-sectional area, d - cable diameter (5 mm).
Portion of the heat flux that goes downward is considered as a waste. The efficiency of the underfloor heating can be estimated as a ratio of heat flux directed upward to the total produced heat power.
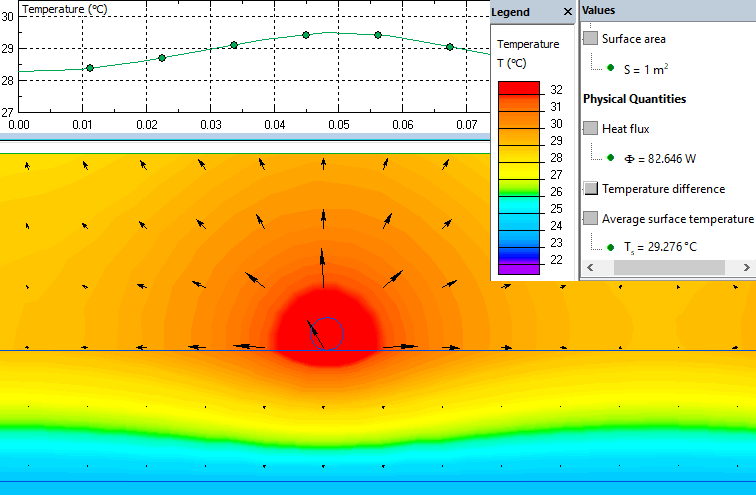
Results
The cable is laid in such a way that the total heat power is 100 W/m². The upward-directed heat flux is 83% of the total power produced by the cable. Then 17% of the heat flux goes downward.
The average floor surface temperature is 29°C.
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).