Cogging torque
QuickField simulation example
Here we will review an example of poor design of the wind turbine generator. Number of rotor poles is chosen to be 2p=12. It turns out that the ratio of the number of stator slots (Z1 = 48) to the number of rotor poles is an integer.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of DC magnetics.
Geometry
Axial length is 400 mm.
Given
Stator slots number Z1 = 48
Rotor poles number 2p = 12
Permanent magnet coercive force Hc = 950 kA/m
The B-H curve for the stator and the rotor:
Task
Calculate the cogging torque.
Solution
Cogging torque* is a result of permanent magnet magnetic field and the stator core interaction. We do not specify current in the stator armature and measure the torque for a set of rotor positions. The calculations are automated using the LabelMover parametric tool.
Results
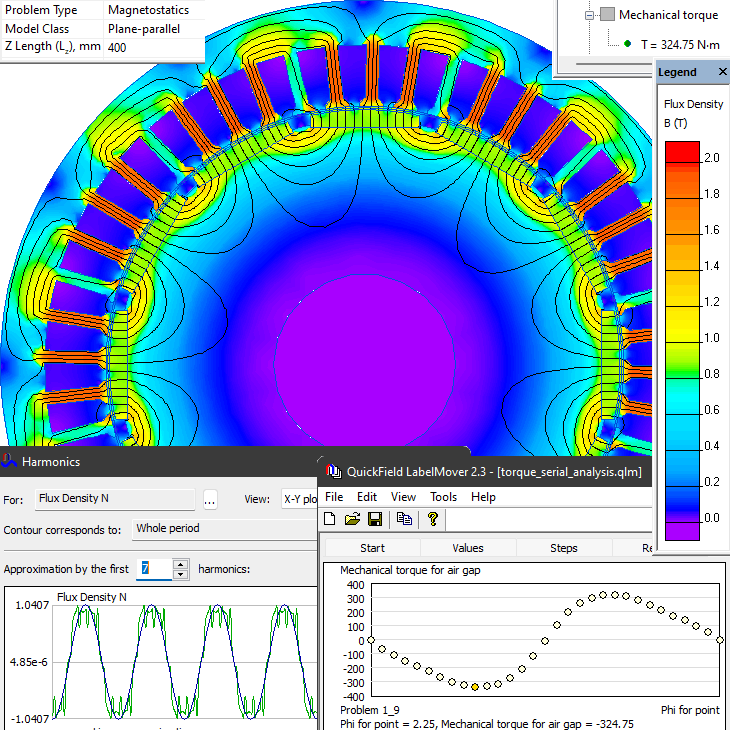
Airgap flux density fundamental harmonic is 1.04T. Cogging torque peak value is 324 N*m per 400 mm of the generator axial length.
Field picture of the flux density distribution and the fundamental harmonic magnitude.
Reference
*Wikipedia: Cogging torque
- Video: Cogging torque. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).