Halbach array generator voltage
QuickField simulation example
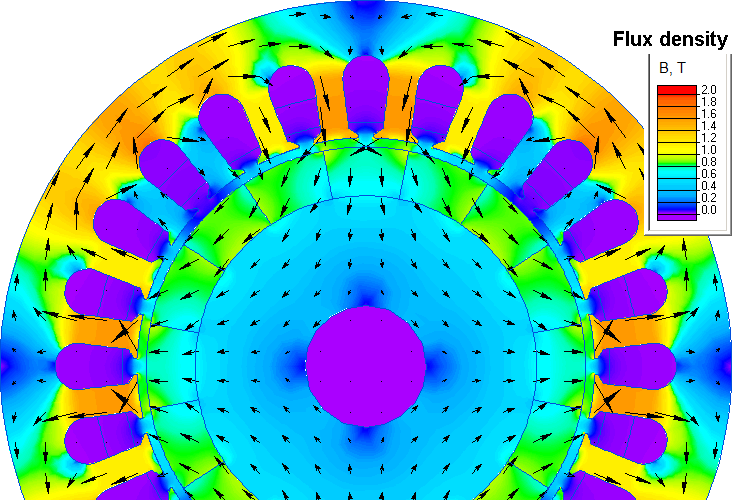
The excitation of the magnetic system on the rotor side is due to the Halbach assembly. The Halbach array is a special arrangement of permanent magnets that increases the magnetic field on one side of the assembly while cancelling it to near zero on the other side.
Problem type:
Plane-parallel problem of DC magnetics.
Geometry
Axial length is 50 mm.
Given
Stator phase coil number of turns w = 90,
Coercive force of permanent magnets 730 kA/m,
Rotor poles 2p = 4,
Synchronous rotation speed n = 750 rpm.
Task
Calculate the idle generator electromotive force (EMF).
Solution
In no-load there is no electric current in the winding, the output voltage is equal to the induced electromotive force.
First in QuickField we measure the flux linkage with half-coils Φ_A, Φ_a, Φ_B, Φ_b, Φ_C, Φ_c as a function of rotor angular position. We get this dependency automatically using the LabelMover parametric calculation utility. Then the phase winding flux linkage is calculated: Φ_Aa = Φ_A-Φ_a, Φ_Bb = Φ_B-Φ_b, Φ_Cc = Φ_C-Φ_c.
The electromotive force is calculated as the ratio of the flux linkage increment ΔΦ to the angle increment Δφ:
EMF = -w * dΦ/dt = -w * ΔΦ / (Δt), where time increment is related to the angle increment Δφ as: Δt = (Δφ/360) / (n/60).
Result
In LabelMover we set the angle increment to be Δφ = 1 degree. The time required to rotate the rotor by 1 degree is Δt = (1/360) / (750/60) = 2/9 ms.
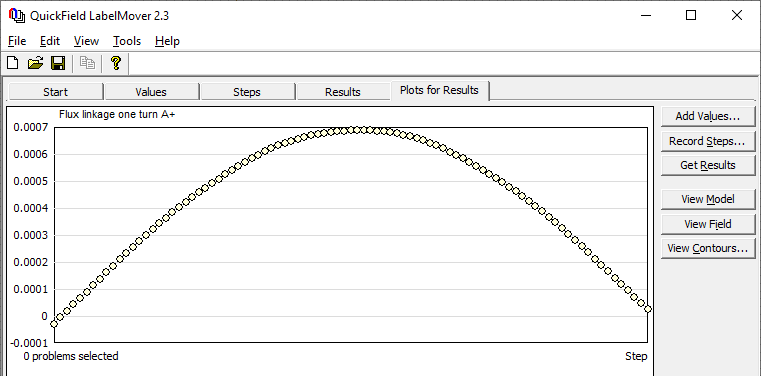
The caculated EMF is non-sinusoidal. Amplitude of the fundamental harmonic was computed with a harmonic analyzer tool: U1 = 19 V.
Magnetic flux density distribution in the permanent-magnet generator
- Video: Halbach rotor generator. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).