Pole shoe optimization
QuickField simulation example
A synchronous salient-pole generator is simulated. The influence of the pole shoe face shape on the flux density harmonics in the air gap is studied.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of DC magnetics.
Geometry
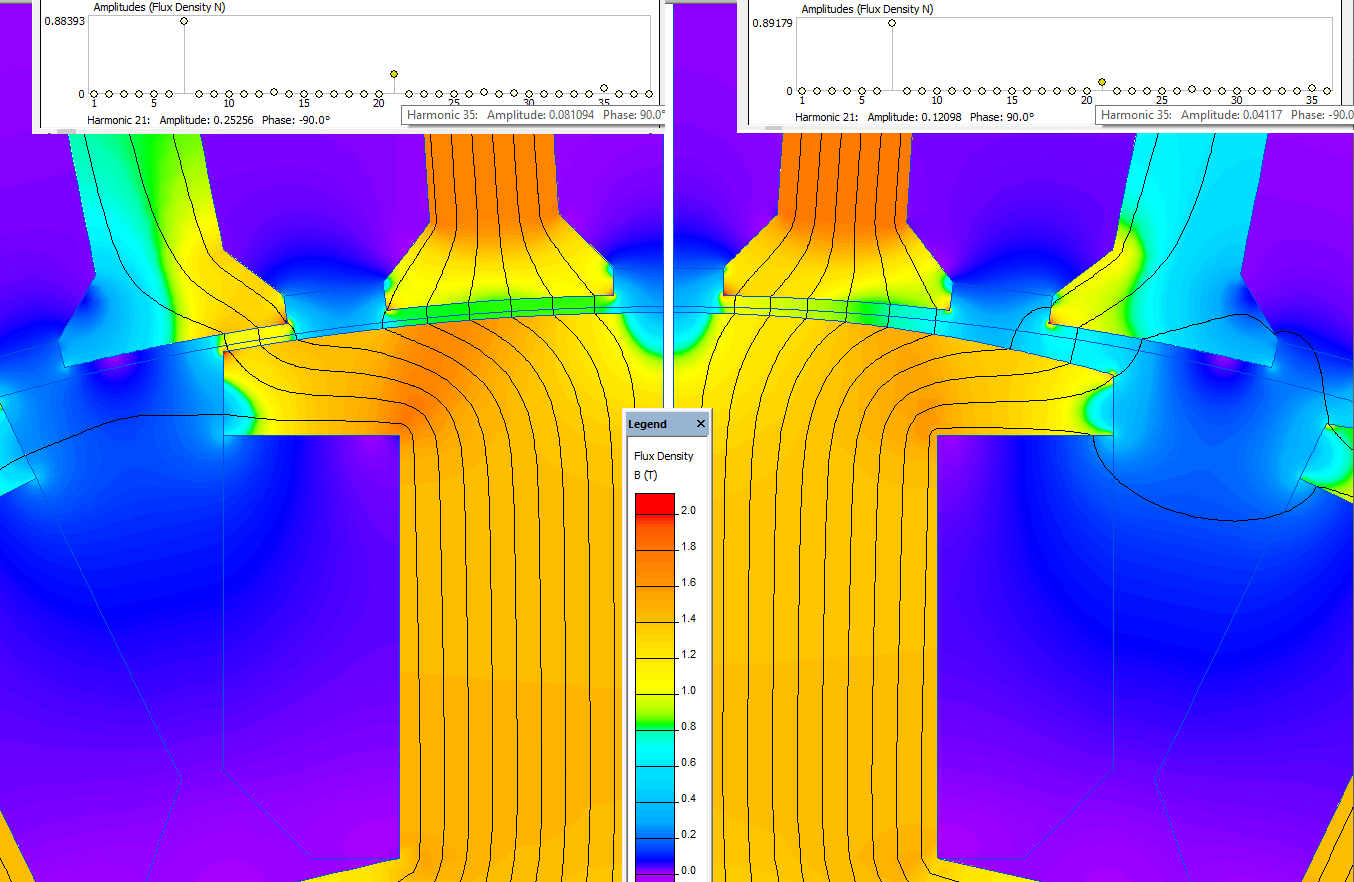
Pole shoe #1 features a constant air gap.
Pole shoe #2 curvature radius is smaller than rotor circumference radius leading to uneven air gap.
Given
Stator slots number Z1 = 48
Rotor poles number 2p = 14
Excitation winding current density j = 4 A/mm²
The B-H curve for the stator and the rotor:
Task
Calculate air gap flux density harmonics for two synchronous motors with different pole shoe designs.
Solution
Both motor cross-sections are included into a single geometry model.
The Harmonic browser addin is used to calculate harmonics. Due to uneven distribution of stator slots and rotor poles we have to use the entire circumference, which includes p=7 periods. Thus the fundamental harmonic number is 7, third harmonic number is 21 and so on.
Results
Magnitude of the pole shoe #1 fundamental harmonic of the flux density is 0.88 T, third harmonic magnitude is 0.25 T. Pole shoe #2 requires +25% more excitation current value to produce about the same magnitude of the fundamental harmonic of the flux density 0.89 T. At the same time the third harmonic magnitude is much less - 0.12 T.
Field picture of the flux density distribution and the flux density harmonic spectrum.
- Video: Pole shoe optimization. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).