Relay dynamics simulation using Python and Parametric Object Interface
QuickField simulation example
The electromagnetic and spring forces act on the plunger. Both forces depend on the plunger position. Calculate plunger motion function.
To combine the electromagnetic field analysis with the moving core dynamics both Python and LabelMover are used. Interaction between LabelMover and Python is performed using application programming interface (API).
Problem Type
Axisymmetric problem of DC magnetics.
Geometry
Given
Current I = 400 Ampere*turns;
Plunger pull-out position xmax = 10 mm.
Plunger pull in position xmin = 6 mm.
Plunger weight m = 4.5 g;
Spring constant k = 4 N/m
Spring free position xspring.free = 15 mm.
Task
The electromagnetic and spring forces act on the plunger. Both forces depend on the plunger position. Calculate plunger motion function.
Solution
The multi-turn winding is replaced with the equivalent total current.
The motion function can be found from second-order differential equation
m · d²x/dt² = f(x),
where m - is a plunger weight (kg),
x - is a plunger position (m)
f(x) - is the force acting on the plunger (N).
The force acting on the plunger is a sum of spring force fspring(x) = k·(xspring.free - x) and electromagnetic force.
The equations are solved in Python. The dynamic link through win32com is used to invoke LabelMover and calculate the electromagnetic force at each step.
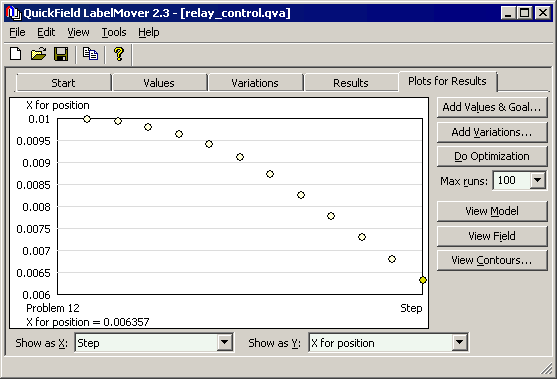
The calculations are stopped when x=xmin (pull in position, plunger hits damper).
Results
The plunger hits initial position between 11th and 12th steps (0.055 - 0.06 s).
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).