Turbine generator synchronous inductance
QuickField simulation example
The magnetic reluctance of the rotor varies along its d- and q-axes. As a result, stator armature inductance varies with the rotor angular position. When the rotor d-axis is parallel to the stator magnetic field, the inductance value is maximum and is referred to as synchronous inductance.
Problem Type
Plane-parallel problem of DC magnetics.
Geometry
Axial length is 5400 mm.
Given
The B-H curve for the tooth zone:
The B-H curve for the rotor and stator yoke:
Task
Calculate phase coil inductance.
Solution
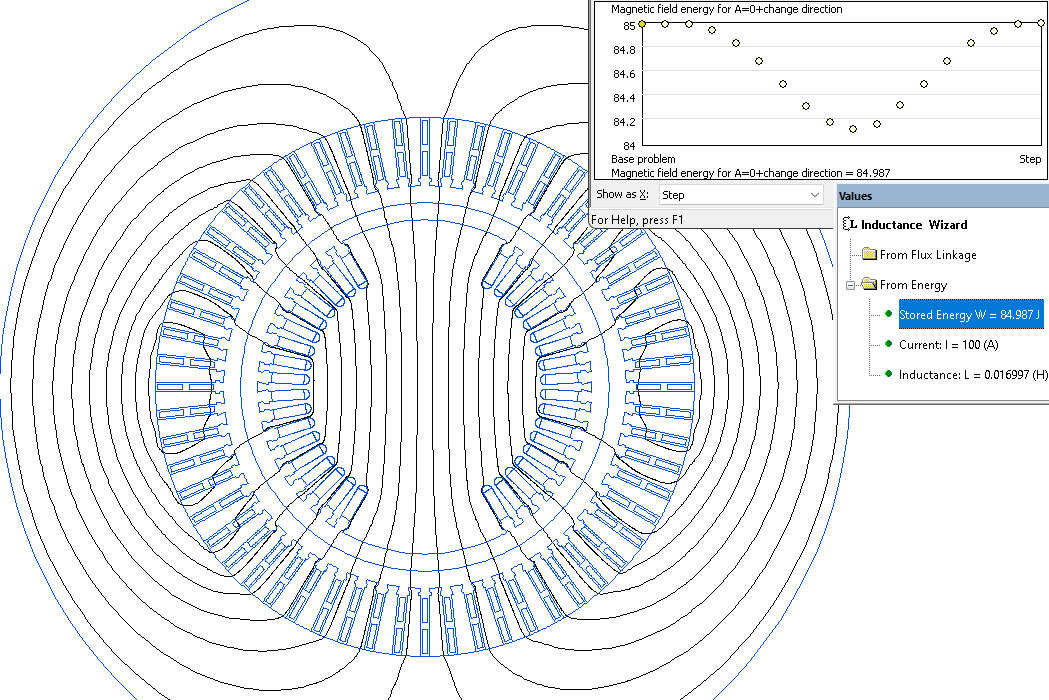
Only the A-X coil is energized by direct current to calculate a phase coil inductance. The magnetic field energy is measured:
Inductance = 2* Energy / Current²
To obtain the maximum inductance value, we solve a series of problems with varying rotor angular positions.
A LabelMover parameterization tool is used to automate the generation and analysis of a series of problems.
Results
Synchronous inductance Ld = 0.017 H.
- Video: Synchronous inductance. Watch on YouTube
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).